Describing motion
Speed To calculate the average speed of an object, we can use the following equation: Where: Rearranging the speed equation
Speed is a measure of how fast an object moves. We need two things to calculate the average speed of an object:

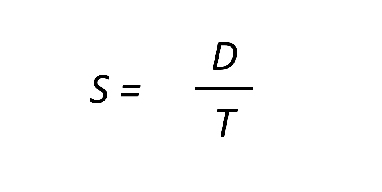
You might also need to find the distance or time, not just the speed. So, you need to know how to change the formula to get different answers.
The formula triangles below show you how to find speed, distance and time: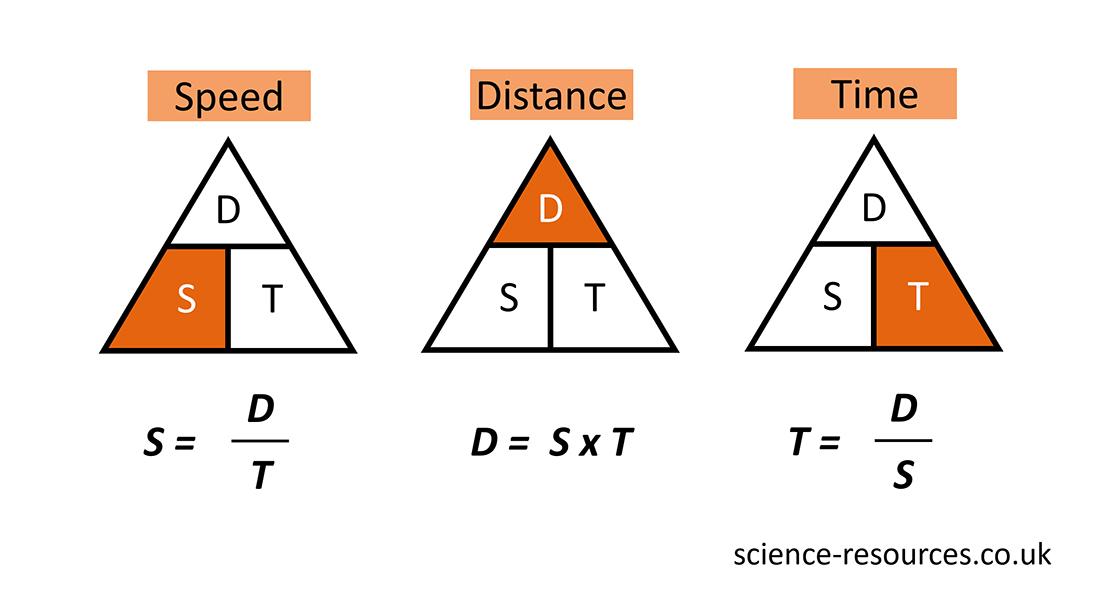
Plotting the speed of an object As you can see from the graph above, time (s) is plotted along the the x-axis and distance (m) is plotted along the the y-axis. The direction and slope of the lines provide information about the speed of the object. Relative motion Formula for relative speed Objects moving in opposite directions towards, or away from, each other. Relative speed = speed of object 1 + speed of object 2 Objects moving in the same direction. Relative speed = fastest speed – slowest speed
The unit for speed is metres per second (m/s). This can be represented on a distance-time graph.
Distance-time graph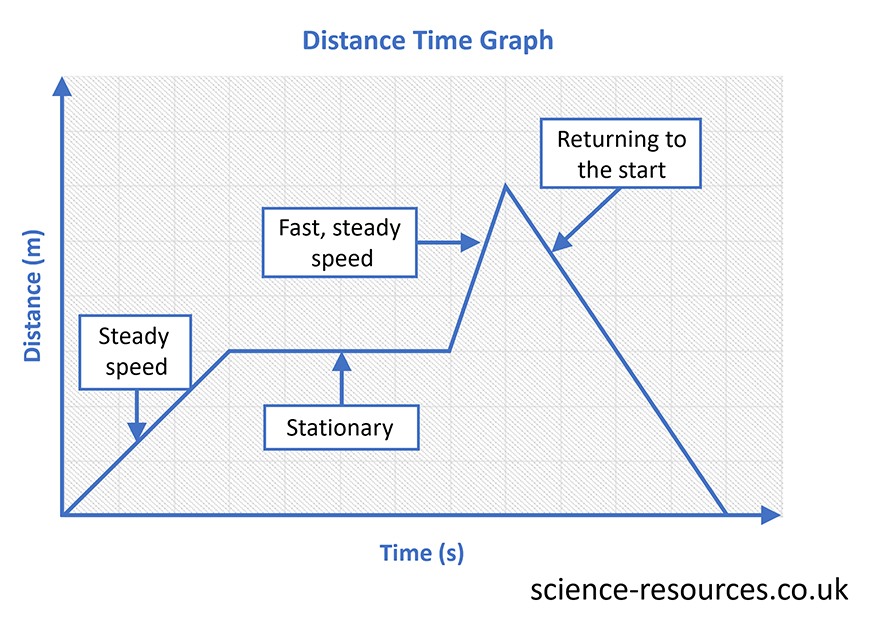
When you are in a car on the motorway, you might see other cars pass by slowly, even though you know they are moving very fast. This is because of how they move compared to you.
How you find their relative speed depends on if they’re moving in the same direction or the opposite direction. The table below shows us how to do this:
Scenario
Summary: